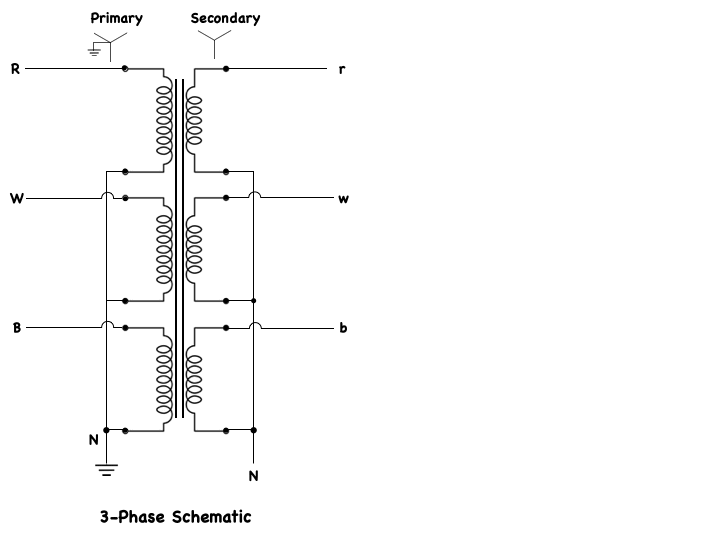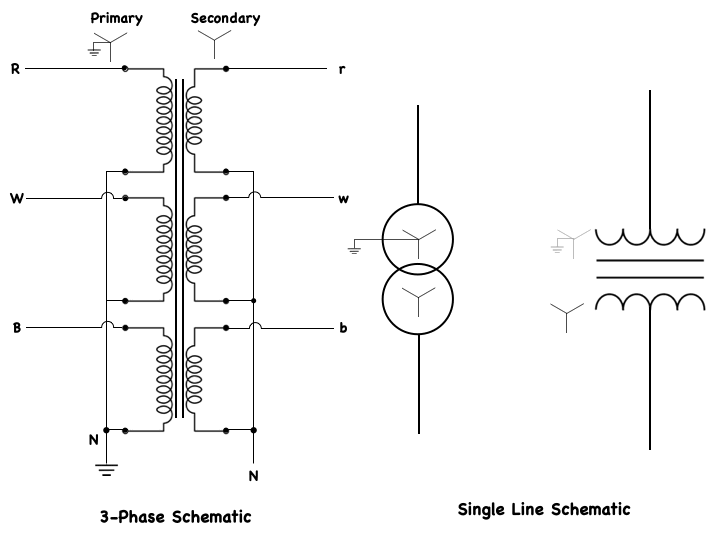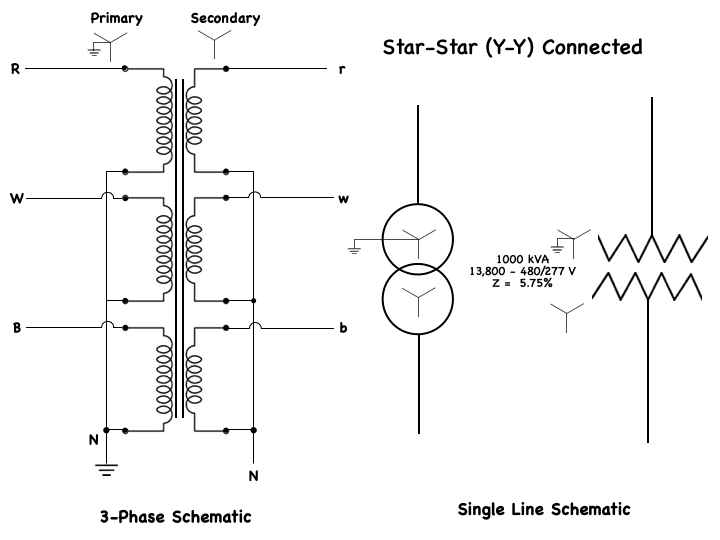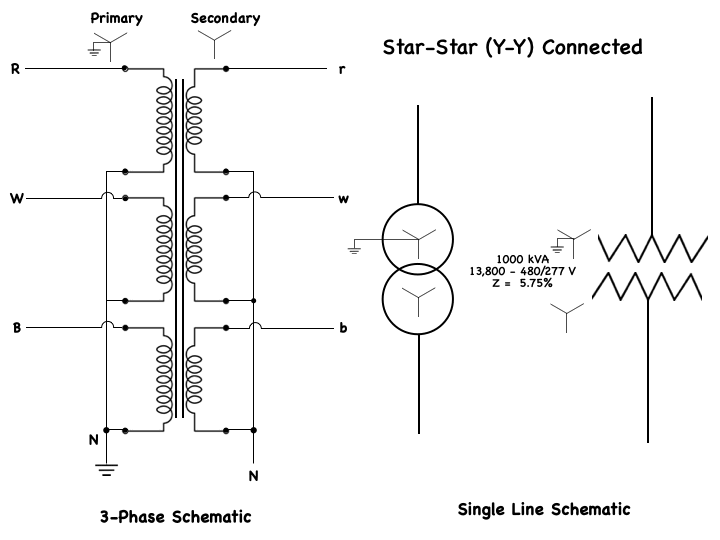
Most electrical power, when produced at power plants, is produced as three-phase AC voltage. Electrical power is also transmitted in the form of three-phase voltage, over long-distance power-transmission lines.
At its destination, three-phase voltage can be changed into three separate single-phase voltages for distribution into the residential areas. Although single-phase systems are used mainly for residential power distribution systems, there are some industrial and commercial applications of single-phase systems. Single-phase power distribution usually originates from three-phase power lines, so electrical power systems are capable of supplying both three-phase and single-phase loads from the same power lines. This 3-Phase schematic shows a typical power distribution system from the power station, or (source) to the various single-phase and three-phase loads that are connected to the system.
The above drawing shows a single-phase power distribution system, at (A) is a Single-phase, two-wire system, at (B) is a Single-phase, three-wire system (taken from two hotlines) and at (C) is a Single-phase, three-wire system (taken from one hot line and one grounded neutral).
Single-phase systems can be of two major types. a single-phase two-wire system, which is shown in “A”, (the top diagram), or a single-phase, three-wire system, which is shown in “B” and “C”, (the middle and bottom diagrams). These systems shown here us 10 KVA, 20 KVA, and 30 KVA transformers whose secondary produces single-phase voltages, such as 120 and 240 volts.
In early residential distribution systems, single-phase two-wire system were the type most used to provide 120-volt service. However, as appliance power requirements increased, the need for a dual-voltage system was evident.
To meet the demand for more residential power, the single-phase three-wire system is now used. A home service entrance can be supplied with 120 240-volt energy by the methods shown in “B”, and “C”, (the center and bottom diagrams). Each of these systems is derived from a three-phase power line. The single-phase three-wire system has two hotlines and a neutral line. The hotlines, whose insulation is usually black and red, are connected to the outer terminals of the transformer secondary windings. The neutral line (the white insulated wire) is connected to the center tap of the distribution transformer. Thus, from neutral to either hotline, is 120 volts that may be obtained and used mainly for lighting and low-power requirements.
All of the aforementioned information is given in this one concise three phase schematic drawing.